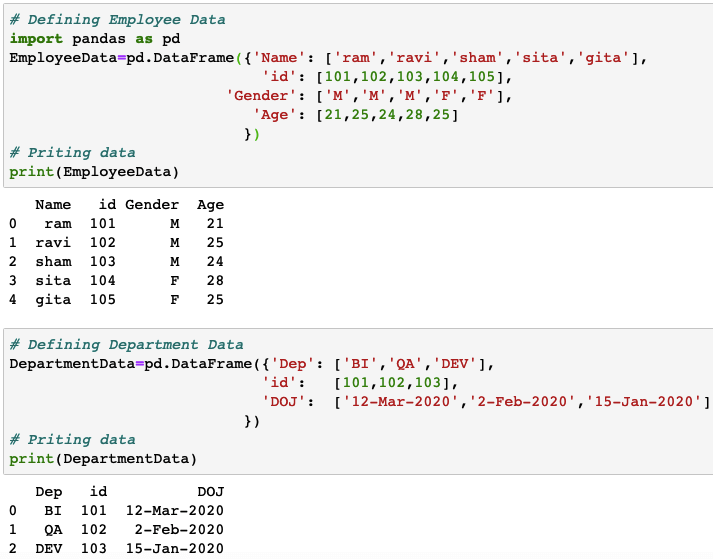
You can perform SQL-style join between two pandas data frames as well! all you need is one common column in both the data frames. In SQL it is known as the primary key.
In the below example, two data frames are joined based on the common key “id”.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
# Defining Employee Data import pandas as pd EmployeeData=pd.DataFrame({'Name': ['ram','ravi','sham','sita','gita'], 'id': [101,102,103,104,105], 'Gender': ['M','M','M','F','F'], 'Age': [21,25,24,28,25] }) # Priting data print(EmployeeData) # Defining Department Data DepartmentData=pd.DataFrame({'Dep': ['BI','QA','DEV'], 'id': [101,102,103], 'DOJ': ['12-Mar-2020','2-Feb-2020','15-Jan-2020'] }) # Priting data print(DepartmentData) |
Sample Output:
Inner Join
An inner join will combine all the columns of the first data frame with the second where common values of ‘id’ columns are found.
|
1 2 |
# Performing Inner Join EmployeeData.merge(DepartmentData,how='inner',on=['id']) |
Sample Output:

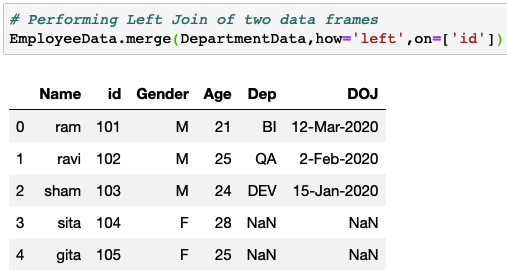
Left Join
A left join will keep all the rows from the first data frame and put NA for corresponding missing column values in the second data frame based on the common column. In the below example there were no records for id=104 and 105 in the second data frame, hence the values became NaN.
|
1 2 |
# Performing Left Join of two data frames EmployeeData.merge(DepartmentData,how='left',on=['id']) |
Sample Output:
Right Join
Right join will keep all the rows of the second data frame and try to find the corresponding rows in the first data frame based on the common column.
In the below example, the second data frame has only 3 rows and all the ids are present in the first column as well, hence, the corresponding values will be fetched.
|
1 2 |
# Performing Right Join of two data frames EmployeeData.merge(DepartmentData,how='right',on=['id']) |
Sample Output:

What if there is no common column?
If there are no common columns between two data frames and still you want to add few columns from one data frame to another, then you can simply select those columns from the source data frame and assign it to the target data frame.
In the below example, EmployeeData does not has “Dep” and “DOJ” columns, if you simply want to add it without using any common column then simply select those two columns from the DepartmentData and assign it to the EmployeeData.
The only thing you need to understand is, the number of rows must be the same in both the data frames, otherwise, NaN values will appear in place of missing rows as shown in the below example.
|
1 2 3 |
# Adding columns from another data frame without common column EmployeeData[['Dep','DOJ']]=DepartmentData[['Dep','DOJ']] EmployeeData |
Sample Output:


