Sometimes you need to get only few rows or only a few columns from the data or a mix of both. This is known as data filtration or data subsetting.
Getting a part of data based on certain conditions is a daily task for a Data Scientist! Pandas has good filtering mechanisms which are vector based, fast and easy to formulate!
Listing down some of the most commonly used filtering mechanisms for Data Frames
- Extracting only one column
- Extracting multiple columns
- Extracting rows based on a condition on a single column
- Extracting rows based on conditions on multiple columns
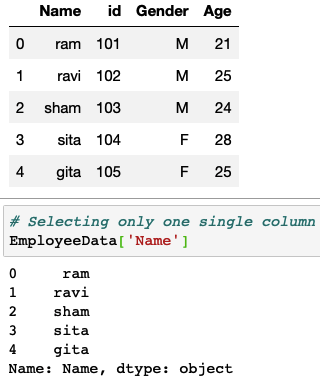
Extracting only one column from a data frame
This is the simplest form of subsetting, all you need to do here is provide the name of the column as a string variable as shown below.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
# Defining sample Employee Data import pandas as pd EmployeeData=pd.DataFrame({'Name': ['ram','ravi','sham','sita','gita'], 'id': [101,102,103,104,105], 'Gender': ['M','M','M','F','F'], 'Age': [21,25,24,28,25] }) # Priting data print(EmployeeData) # Selecting only one single column EmployeeData['Name'] |
Sample Output:
Extracting Multiple columns from a data frame
When you want to extract multiple columns, you can pass the names of columns as a list. There are two options, either you can pass the list of columns directly or store the list as a variable and pass that variable.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# Selecting multiple columns EmployeeData[['Name', 'Age']] # Selecting multiple columns by list as a variable selectedCols=['Name', 'Age'] EmployeeData[selectedCols] |
Sample Output:

Extracting rows based on a condition on a single column
A filter condition in python looks more like an english statement!
Below statement shows the boolean vector output created by a condition statement in python
In the example below, you are comparing if the Age of the employee is greater than or equal to 24 or not. You can see in the boolean vector output, it says True if the condition evaluates is true otherwise it says False.
This information can be stored and passed to the data frame for filtering and getting only those rows where the condition was True.
|
1 2 3 |
# Checking if every value present in Age column # is greater than or equal to 25 or not? EmployeeData['Age']>=25 |
Sample Output:

Now using the condition and extracting only those rows where Age is greater or equal to 25
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# Storing the Filter condition as a variable AgeFilter=EmployeeData['Age']>=25 # Subsetting the data based on filter EmployeeData[AgeFilter] |
Sample Output:

Extracting rows based on conditions on multiple columns
You can also combine multiple conditions to filter data. These conditions can be combined in below listed waus
- AND operation: Both conditions must be true
- OR operation: Either of the conditions can be true
AND operation gives lesser rows because it has to satisfy all the conditions.
OR operation on the same conditions gives more rows as it has to satisfy any of the conditions.
In below example Its shown how to extract rows satisfying two conditions like Age>=25 and Gender is Female.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
# Storing the Filter condition as a variable AgeFilter=EmployeeData['Age']>=25 GenderFilter=EmployeeData['Gender']=='F' # Subsetting the data based on multiple filters # Age >=25 AND Gender is Female print(EmployeeData[AgeFilter & GenderFilter]) # Subsetting the data based on multiple filters # Age >=25 OR Gender is Female print(EmployeeData[AgeFilter | GenderFilter]) |
Sample Output:


